Principle:
Optochin (ethyl hydrocupreine hydrochloride) sensitivity test is used for the presumptive identification of alpha-hemolytic streptococci as Streptococcus pneumoniae. Optochin is used to differentiate Streptococcus pneumoniae from other alpha-hemolytic streptococci. Streptococcus pneumoniae strains are sensitive to Optochin although some strains are optochin-resistant and other alpha-hemolytic streptococcal species are Optochin-resistant. The Optochin test is performed on a blood-agar medium using a disk diffusion principle. Optochin sensitive Streptococcus pneumoniae surrounding the disk impregnated with optochin are lysed, due to changes in surface tension, creating a clear zone of inhibition.
Procedure:
- Take a few isolated colonies of the alpha- hemolytic organism and streak onto a blood-agar plate.
- Place an Optochin disk, in the streaked area and incubate it at 35-37oC.
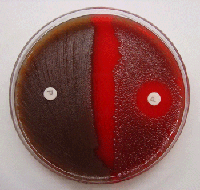
- Examine the plate after 18 – 24 hours of incubation and measure the zone of inhibition if applicable.
Interpretation:
If the zone of inhibition is 14 mm or more, around a 6-mm disk, then identify the organism as Streptococcus pneumoniae. If the inhibition zone is less than 14 mm, further testing (bile solubility or serology) should be done for the identification of Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Quality control
Each new lot of optochin disks should be tested with positive and negative controls.
Positive control – Streptococcus pneumoniae ATCC 49619
Negative control- Streptococcus mitis strain ATCC 49456
Views – 20575
Leave a Comment